Volatility is the amount that a stock moves over a given period of time. At times markets experience periods of low volatility when the difference between the highs and the lows are relatively small. At other times, the market may experience high volatility with wild swings from low to high and back again. Generally, high volatility is related to market uncertainty, news is coming fast, first driving prices and fears up and then something convinces the market that the fears were unfounded so prices fall and then something stirs the fear once again.
Market volatility can be hard on an investor because the wider the swings in an investment’s price, the harder emotionally it is to not worry. But short term traders often like to trade volatile markets because price volatility presents more opportunities to buy assets cheaply and sell when overpriced in a shorter time frame. Of course you need some mechanism to determine when the price is cheap and when it is overvalued.
Volatility does not measure the direction of price changes, simply the difference between the highs and lows. When calculating volatility the standard deviation or variance is used. In this method all differences are squared, so that negative and positive differences are combined into one quantity. Two stocks with different volatilities may have the same expected return, but the stock with higher volatility will have larger price swings over a given period of time. But now it is possible to trade not just based on how volatility will affect the underlying stocks but to trade volatility itself.
In today’s article J.W. Jones looks at trading volatility.
Taking Advantage of Recent Lows in the Volatility Index
One of the newest option products to appear in our universe as an options trader is the option series designed to trade the volatility index (VIX). The VIX is a measurement of the implied volatility of the S&P 500 index.
To review quickly, the implied volatility of an options series is reflective of the aggregate market opinion of the future volatility of a given underlying asset. In terms of the Volatility Index, the price is the current market opinion of the future volatility in the S&P 500 Index over the next 12 months.
As are all attempts to predict the future, this value does not always reflect accurately the actual volatility as it plays out prospectively, but at a practical level it is the best we can do. As sage philosophers have long noted, “the future isn’t what it used to be.”
The importance for traders is the well established and generally known inverse correlation between prices for the given underlying and the measure of implied volatility, in this case our VIX value. What is typically less known is the fact that levels of implied volatility correlate even more closely to the velocity of the price move of the underlying asset in question.
Because rapid price moves occur far more frequently to the downside, it follows that the general correlation between price and implied volatility is inverse. A fundamental characteristic that underscores the logic of this trade is the strong tendency of the VIX to revert to its recent mean. While this is not a certainty, it is unquestionably a high probability outcome.
For professional traders, much of the focus of hedging activity has recently moved to establishing protective positions in this index rather than such older techniques as buying out-of-the-money protective index puts. However there are some well recognized pitfalls in this approach that lay in wait for the retail trader not aware of some of the nuances inherent to this approach.
One of the major risks in trading this product derives from the fact that both options and ETFs are based on the value of VIX futures. Because there is no mandatory mathematical linking of the value of these futures in the several available expiration months as is routinely present in the options series with which most traders are familiar, a huge and not generally recognized risk exists.
The founders of one of the major retail options brokers have repeatedly cautioned that the single major cause of irreparable account ‘blow ups” they witnessed were the result of time spreads, aka calendar spreads, in this VIX product. This is the result of the ability of the various expiration months to move without mutual correlation in response to significant market events.
The result of this observation is the practical consideration that time spreads in the VIX must never be traded. No calendar spreads must ever be considered when trading the VIX. Failure to follow this admonition will subject your account to risk far beyond what you consider to be remotely possible. Simply put, “Don’t do it.”
So what trades in the VIX carry reasonable and definable risk? A wide variety of trades including those with both defined and undefined risk is feasible. Such trades include verticals, butterflies, condors, and simple long and short options.
Long time readers know that I strongly prefer to structure positions to include at least a component of positive theta within my trades. Positive theta simply means that the spread has a component that will benefit from the passage of time. Let us consider a modified butterfly position; this position is commonly termed a broken wing butterfly.
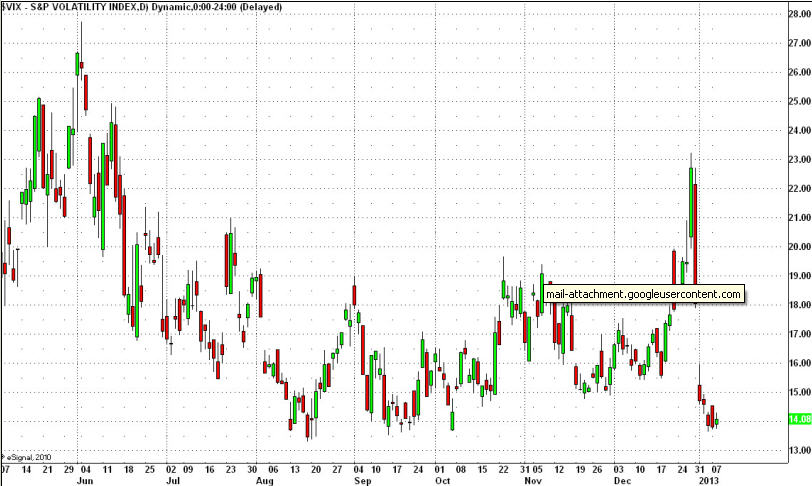
First, let us review the current chart pattern of the VIX:
As can clearly be seen in the chart above, the VIX is at multi-month lows, and perusal of even longer term charts confirm this value is at multi-year lows. Given this situation, the probability of a move upwards toward its recent mean is overwhelmingly high.
In order to give sufficient duration to our trade, I would like to look at a butterfly structure approximately 3 months into the future in order to allow for mean reversion of the VIX.
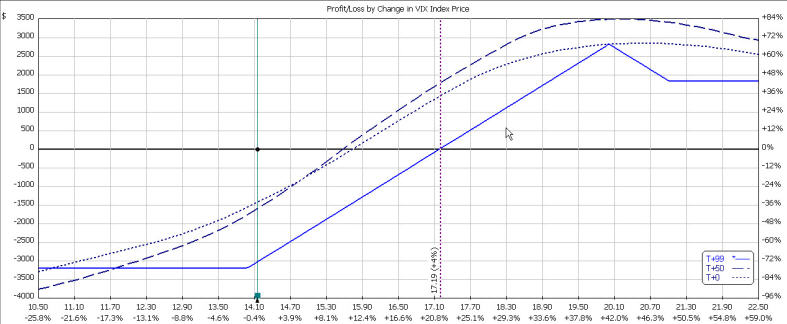
The P&L chart for our broken wing April put butterfly is displayed below:
As can be clearly seen, the trade structure has no upper bound of profitability and the risk to the lower side is the total amount paid to establish the butterfly. As such, this is a defined risk trade that will profit from a reversion of the VIX to its mean.
We welcome you to try our service to see more high probability trades that capitalize on current market conditions. Over the past two years, the service’s performance track record has steadily beaten the S&P 500 Index while taking significantly less risk.
This material should not be considered investment advice. J.W. Jones is not a registered investment advisor. Under no circumstances should any content from this article or the OptionsTradingSignals.com website be used or interpreted as a recommendation to buy or sell any type of security or commodity contract. This material is not a solicitation for a trading approach to financial markets. Any investment decisions must in all cases be made by the reader or by his or her registered investment advisor. This information is for educational purposes only.
This article was originally published at Options Trading Signals and is reprinted by permission.